WDM is a new technology widely used in optical network nowadays, with which you may be not very familiar. The word of WDM is the acronym of wavelength-division multiplexing. As its name implies, it is the technology of using different wavelengths of light to multiplex two or more optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber, to some extent, strongly multiplies the capacity of the network. In its working process, without using additional fibers, optical carrier signals with different wavelengths are combined, transmitted together, and separated again through the single optical fiber. Meanwhile, each signal with different wavelength in the process does not interfere with each other as shown in the following figure. It takes great advantage of the enormous bandwidth of the optical fiber and makes bidirectional communications via one strand of fiber possible.
With the rapid growth of the optical network, the communication exponentially increases, which has used many spare fiber cables installed with the optical network design. However, the spare fiber cables can’t meet the increased communication need and new capacity for the network is still required. How to solve this? At present, there are three methods to expand the capacity of our network: installing more fiber cables; increasing system bitrate to multiplex more signals and wavelength division multiplexing.
As for installing more fiber cables, it is popularly and largely used nowadays, for the cables are inexpensive and the installation is effective under currently advanced technology. But when conduit space is not available or major construction is necessary, the fiber optic cabling would be very complicated with high cost.
As for increasing system bitrate, considering that most of our systems have already worked in 2.5 GB/s network and need to upgrade to 10 GB/s network, which should change out all the electronics in our network. Hence, it is turned out to be an expensive way to multiplex more signals.
Compared with the previous methods, as WDM technology is developed fast and tended to be mature, using this method to expand the capacity of your network is a quite advisable, cost-effective way without adding cables or upgrading network. In simple terms: WDM creates virtual fibers, which is the best and simplest way to multiply fiber capacity in optic network.
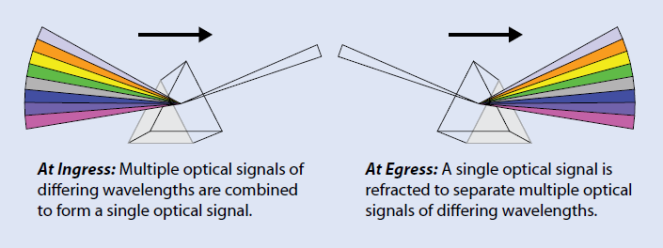
As we all know about the working principle of a prism, when a white light beam moves from the air to the glass, a phenomenon of light dispersion occurs. The refractive index of glass varies with the different wavelengths of light, which makes the light with different wavelengths refracted differently and leave the prism at different angles, creating an effect similar to a rainbow. What should be noted is the process of light beam’s moving from the glass to the air, which is completely reverse. That’s to say, kinds of different color light pass through the prism that will be changed into a white light beam.
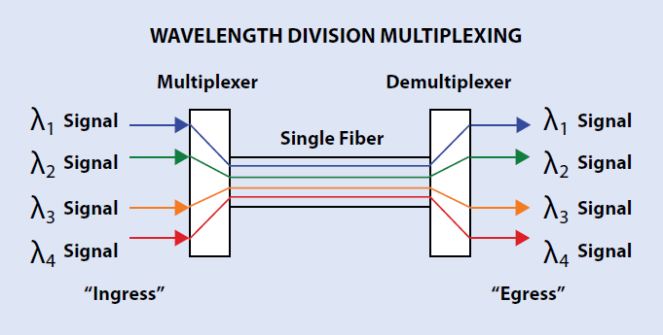
The working principle of WDM technology is the same as the prism. When multiple optical signals of differing wavelengths pass through the ingress, they will be combined into a single optical signal and transmitted together through a single optical fiber. In the transmission process, each signal with different wavelength does not interfere with each other. Once the single optical signal arrives at the egress, it will be separated into multiple optical signals of differing wavelengths again. To help you better understand the working principle of WDM technology, the following figure shows how does WDM use the different wavelengths of light to multiplex signals onto one single optical fiber.
The first WDM system uses a multiplexer at the transmitter to join the two signals together, a single fiber cable for signal transmission and a demultiplexer at the receiver to split the signals apart, which already enables the capacity of the network to be expanded without more fibers. At that time, the WDM system provides two channels over the single fiber cable for two normal wavelengths 1310 nm and 1550 nm. This system is also called normal WDM system or BWDM system sometimes.
The normal WDM system is too expensive to be largely deployed, which also has a very complicated working process. In order to optimize its function and reduce its fabrication cost, there are two superior WDM systems that are being developed sequentially for different applications, coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) systems and dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) systems.
CWDM and DWDM are divided according to different wavelength patterns. In general, CWDM is designed to increase channels on one fiber cable for more wavelengths which varies from 1470 nm to 1610 nm, while DWDM supports the denser channels for wavelengths varying from 1547.72 nm to 1553.33 nm. The words “coarse” and “dense” reveal the difference in channel spacing. That is, the channel spacing for CWDM is 20 nm, as it for DWDM is denser, 0.8 nm. For the details of the basic difference between CWDM and DWDM, you can learn it from the following figure.
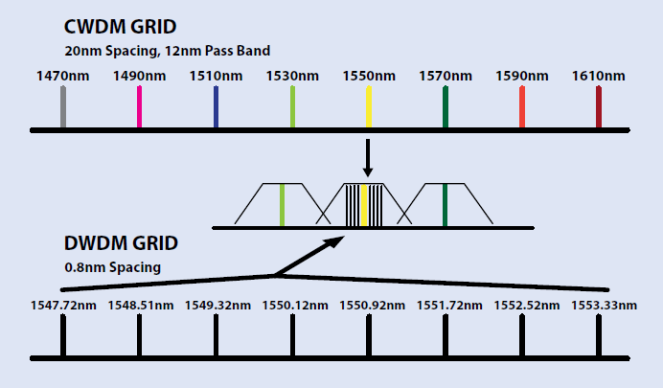
CWDM and DWDM work with the same principle of multiplexing different wavelengths of light via a single fiber, but differ in wavelength patterns. The spacing of the wavelengths, the number of channels, and the ability to amplify the multiplexed signals are different, which are designed to be used for different application.
As for CWDM, it has a wider channel spacing which allows less sophisticated transceiver designs to be used with lower cost. As a result, CWDM is always the first choice for most applications. However, the signals transmitted in CWDM system cannot be amplified that caused a shorter transmission distance, approximately 100km. Taking this into consideration, CWDM is the cost-efficient way for short-distance optical networks.
In contrast to CWDM, there is no doubt that DWDM has a higher performance for its advantage of transmitting a greater number of signals with more stable wavelengths, due to its closer spacing of the wavelengths. Meanwhile, DWDM can also expand greater maximum capacity and transmit the signals longer, thus it is more suitable for long-distance optical networks. Accordingly, DWDM becomes more expensive.
The WDM revolution has already occurred with unanticipated swiftness, which plays an important role in meeting the increasing requirement of modern network. Although WDM technology is lack of a long history, with its great advantages, it is largely used in a really fast manner, dramatically promoting the network for high-volume data transmission over a single fiber cable.
