With the appearance and development of 40/100G Ethernet network, MPO/MTP technology is developed for migrating to 40/100GbE, which is of high density, flexibility and reliability with scalable, upgradeable properties. Do you want to upgrade your system to 40/100G Ethernet network? Are you familiar with MPO/MTP technology? Do you know how to ensure MPO/MTP systems work with correct polarity and why the polarity of the connections using multi-fiber MPO/MTP components from end-to-end should be assured?
Generally, MPO/MTP technology is to pull just one single cable with multiple fibers, which is deployed for multi-fiber applications. When using the technology in 40/100G Ethernet network, only maintaining a correct polarity across the fiber network, could you ensure that the signal transmitted from any of the active equipment can be directed to the receive port of the next active equipment. In order to ensure MPO/MTP systems work with correct polarity, experts develop three methods that will be presented in this paper.
For ensuring proper polarity, experts put forward three polarization methods, which are defined by TIA 568 standard and named as Method A, Method B and Method C. As different polarization methods employ different MPO/MTP trunk cables to connect the fiber network, there are three types of MPO/MTP truck cables with different structures called Type A, Type B and Type C used for the three different connectivity methods respectively. The following will introduce the detailed information of each method with its corresponding truck cable.
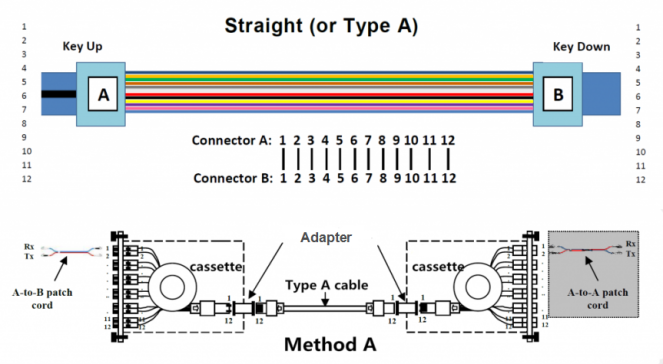
To better understand Polarization Method A, the Type A Trunk Cable should be first introduced that is also referred to as straight cable. It is a straight through cable with a key up MPO/MTP connector on one end and a key down MPO/MTP connector on the opposite end, which makes the fibers at each end of the cable have the same fiber position as shown in the following figure. For instance, the fiber located at position 1 (P1) of the connector on one side will arrive at P1 of the other connector, and the fiber located at P12 on one side will arrive at P12 on the other side.
As for Polarization Method A, it always works with the Type A trunk cable that is designed to connects MPO/MTP modules on each side of the link. The connectivity Method A is also shown in the following figure for your reference.
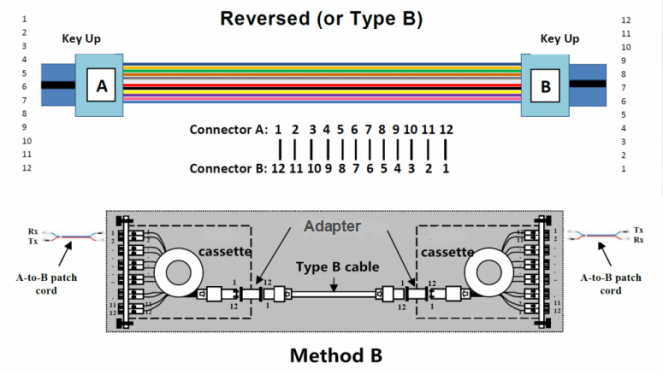
In Polarization Method B, Type B truck cable is used to connect the two modules on each side of the link. Clearly different from Type A trunk cable, Type B trunk cable uses two key up connectors on both ends of the cable, which is known as reversed cable. This mating structure results in an inversion, which means the fiber positions are reversed at each end. For example, the fiber at P1 of one end is mated with the fiber at P12 of the opposing end. From the following figure, you can learn the fiber sequences of a 12 fiber Type B cable and the connectivity Method B.
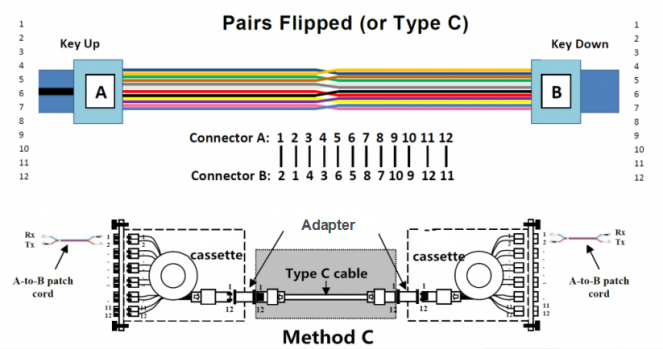
Compared with the previous methods, Polarization Method C is more complicated that works with Type C trunk cable. Type C trunk cable is used for connecting MPO/MTP modules one each side of the link which can be also called pair-reversed trunk cable. You can study the connectivity Method C in the following figure.
Just like Type A trunk cable, Type C trunk cable also has one key up connector and one key down connector on each side. However, it is more sophisticated because each adjacent pair of fibers are designed to flip at each end. That’s to say, the fiber at P1 on one end of the cable will be shifted to P2 on the other end and the fiber at P2 on one end will be mated with P1 on the opposite end, etc. To help you better understand the fiber sequence of Type C cable, you can take the following figure as reference.
From this paper, we can conclude that there are three polarization methods which are developed to ensure MPO/MTP systems work with correct polarity, and each polarization method has its own trunk cable to connect the modules in each end of the link. If you want to upgrade your system to 40/100G Ethernet network, you can choose the most suitable method for assuring the correct polarity in your fiber network, which will make your system work great.

