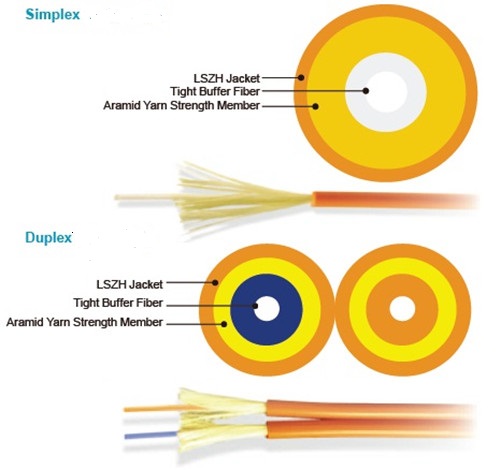
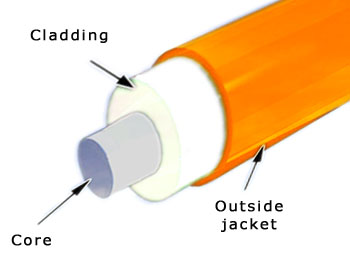
In the optical network deployment, fiber optic termination should be an unavoidable and vitally important procedure that enables fiber cross connection and light wave signal distribution. Only when the fiber optic cables in the network are terminated properly can they be protected from dirt or damage so as to achieve a smooth and steady network. Meanwhile, proper fiber optic termination can efficiently avoid the excessive loss of light when the network runs, which strengthens the smooth connection. But how to properly terminate fiber optic cables to ensure a smooth connection? Let’s talk about this topic and find the most suitable method to terminate fiber optic cables for your network.
There are two methods for terminating fiber optic cables, using connectors and splicing, each of which allows for a smooth connection with low light loss and back reflection in a proper manner. We can learn these two methods in the following figure. The method of using connectors to terminate fiber optic cables is shown in the top right corner that is able to mate two fibers for a temporary joint, while the other method is splicing which has the ability to create a permanent joint between the two fibers. As for the step-by-step instructions of these two methods, it will be introduced detailedly in the following text.

You may often hear about the descriptions like LC to LC patch cord, LC to SC patch cord and LC to FC patch cord when choosing fiber patch cords to deploy your network. Do you understand what do the words “LC” “SC” and ”FC” mean? In fact, they stand for three kinds of connectors that are to terminate the ends of fiber optic cables, with the aim of connecting and disconnecting two fibers for many times without affecting the optical performance of the fiber circuit. To get a smooth fiber circuit, the following will illustrate how to use the connectors to properly terminate fiber optic cables.
-
Take out the fiber optic cable that you want to terminate and prepare a fiber cleaver for the termination.
-
Strip away the outer jacket, buffer and cladding of the fiber optic cable and cut away the excess aramid yarn.
-
Lightly score the fiber by pressing the fiber cleaver. Don’t use the cleaver more than once to score the fiber, so that the fiber will not be broken by unexpected, additional notch.
-
Along the score, bend the fiber and the tongue of the cleaver together to break the fiber.
-
Use the scale on the cleaver for measuring the bare fiber to ensure that it is long enough, so that it can reach the fiber inside the connector and make the termination work finally.
-
Utilize alcohol wipes with at least 90% isopropyl alcohol content and lint-free material to clean the fiber.
-
Carefully insert the bare fiber into the connector and crimp the connector onto the buffer.
Notices: Please check and confirm the right types of connectors and their polishing styles before making the termination to avoid non-corresponding installation. Moreover, test periodically during the installation, rather than testing them all after the job is completed to eliminate the possibility of repeating the same errors throughout the installation.
When the fiber cable is too long or there are various fiber cables that needs to be mixed, the splicing is strongly recommended to do the fiber optic termination. For instance, splicing a 48-fiber cable and six 8-fiber cables together. Meanwhile, if a buried finer cable is accidentally severed, you are also suggested to use the splicing method to restore the fiber optic cable. The following will introduce the procedures of fusion splicing which may be useful for you to make a proper fiber optic termination.
-
Prepare the two fiber ends that need to be spliced together.
-
Strip the protective coating, jackets, tubes, strength members, etc, and only leave the bare fiber showing.
-
Clean the fiber cables and use score-and-break method to score the fibers, for the sake of proper splicing.
-
Properly align the cleaved end-faces of the two fibers, and then utilize an electrical arc to melt them. Hence, the two fiber ends can be permanently welded together.
-
Finally use the heat shrink tubing, silicone gel and mechanical crimp protector to protect the splice from outside elements and breakage.
From the mentioned above information, we can easily acquire two proper methods for fiber optic termination, using connectors and splicing, both of which are the useful and effective solutions to achieve smooth connections. Using these two methods to terminate fiber optic cables can protect the fibers from being damaged, avoid the excessive loss of light and keep a stable performance for your network.